Blog
Machine Translation Report
What is the optimal MT Engine for you? Find out in the latest MT Report by Memsource.

Cloud-based translation tools offer a level of security that until recently was unprecedented in the industry.
While translation data is often confidential in nature, keeping it secure during the translation process has traditionally been extremely difficult. Until cloud-based translation tools arrived on the market, data often had to be forwarded two, three, or four times to unsecure email accounts, and would subsequently be stored on multiple unsecure hard drives. This is clearly an issue for users who want their data to remain safe and confidential.
Here we will highlight the most common workflow scenarios used in translation and the various security issues when compared to using a cloud-based translation tool like Memsource.
1. No Translation Technology Used
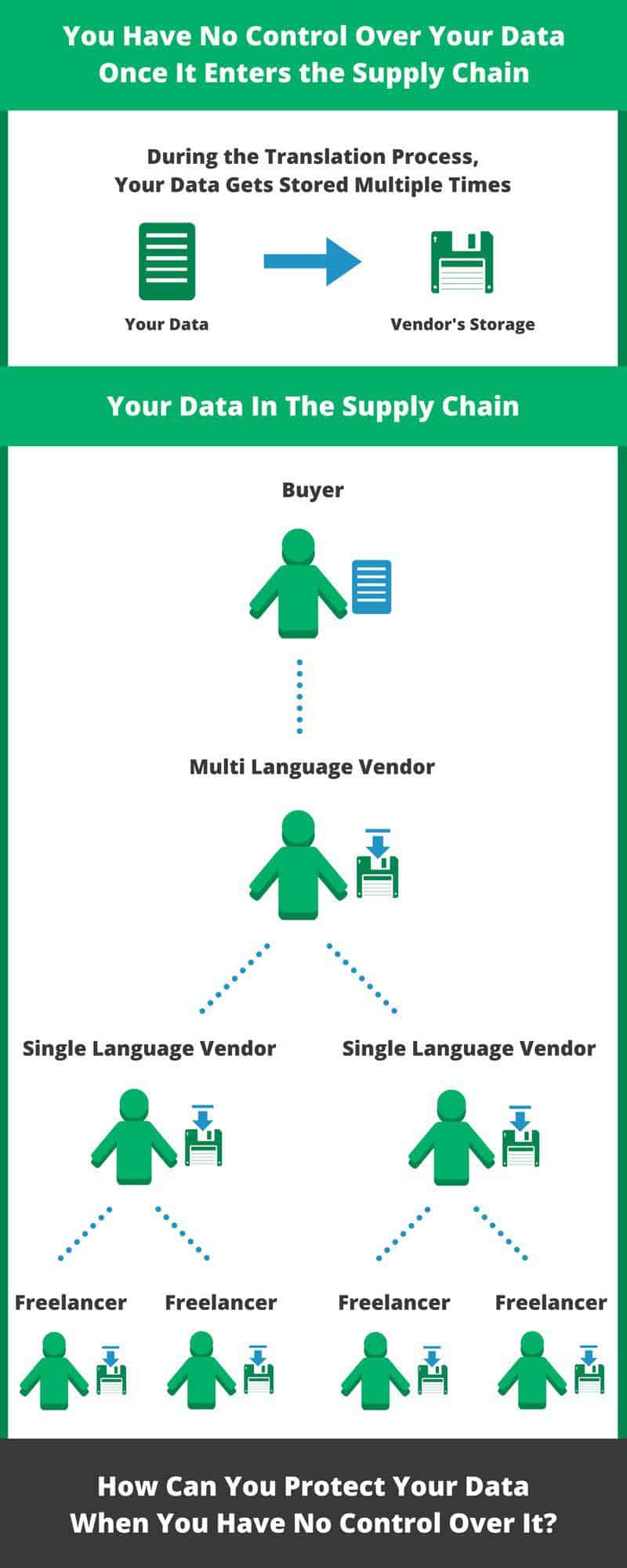
In this first situation, files for translation are distributed by email or FTP. Even if files are password-protected when emailed or when a secure FTP is used, after a client hands over files to a translator or agency, they essentially lose all control over their data. They have no control over who has access to the files, where the files are stored, how many people they are forwarded to, or who will keep them once the process is complete.
For example, a file for translation can easily travel from the client, to a large translation agency, to a smaller, specialized translation agency, then on to a freelance translator, and so on. In this scenario, multiple copies of the file are stored on multiple devices with absolutely no client control of the data. As a result, the level of security in this situation is almost nonexistent. However, this is still a very common scenario in today’s workflow because the translation industry is traditionally very decentralized.
2. Desktop Translation Technology
Another common scenario is that of desktop translation technology. Some clients own a desktop translation product on which they maintain vital translation resources, such as translation memory, a term base, and the actual files for translation. The typical scenario in this case would be similar to the first one - the desktop translation tool exports a bilingual file for translation which is then sent via email or FTP to the translation agency, and the same chain of file sharing follows. In this scenario, the translation agency also needs a translation tool that is able to process the bilingual file for translation. Most likely, the content of the file will then be stored in the translation memory of the agency, along with its sub vendors and the actual freelance translator they use for the translation.
While a desktop translation product may increase translation efficiency, it also causes additional security risks as the entire translation (both source and target) will be stored in several translation memories, most likely for a very long time. There is a strong possibility that the content will be re-used for the client’s future translation purposes, and also possibly for translations by other clients of the freelance translator. Very often, freelance translators keep just a single translation memory in which they store the translations of all their clients.
3. Client Server Technology
Client-server translation technology is a big step in the right direction. If a client owns a server-based translation product, the level of control dramatically increases compared with the previous two scenarios, as everything is edited and stored locally on a siloed system. Unfortunately, the number of clients who own and maintain a translation server product is very small, since significant financial resources are required to buy the server and to hire well-trained staff to operate and maintain the technology. Furthermore, most client-server products do not make it possible or easy to keep the same level of security throughout the entire translation workflow. Very often, a bilingual file will need to be exported for translation at some point, such as when a translation agency hands over a task to its freelancer. At this point, the level of security decreases dramatically and is similar to the second scenario. The freelance translator will be required to processes the file on their PC locally, including storing all the data into their translation memory.
4. Cloud Technology
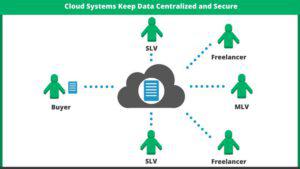
Cloud-based tools change the game entirely. They work similar to their server-based predecessors, except instead of everything being stored and edited on a local server, it is done online, or on ‘the cloud’. Regarding security, this means that a file never needs to be emailed or stored in an unsecure location and data owners maintain full control over their translation material from start to finish. The owner sets access rights which can be revoked at any time and has the power to prohibit downloads for highly confidential documents. Translators can be directed to a web based editing tool to work in, meaning no data needs to be stored locally on third-party devices.
Data is only stored on the cloud servers which are typically located in high security data centers. Customer data can be encrypted, both at rest (when stored on a server) and in transit (when being sent to a user’s browser), including in highly decentralized scenarios when translation tasks are outsourced to a translation agency that further outsources it to its sub vendors. In these ways, cloud-based translation tools provide some of the most effective security currently to be found in the translation industry.
Start translating securely in the cloud today. Sign up for a free trial of Memsource.